Overview of Preble Efficient Distributed Prompt Scheduling for LLM Serving
It’s all about prompting
Prompt example Complexity of change vs task accuracy
Complexity of change vs task accuracy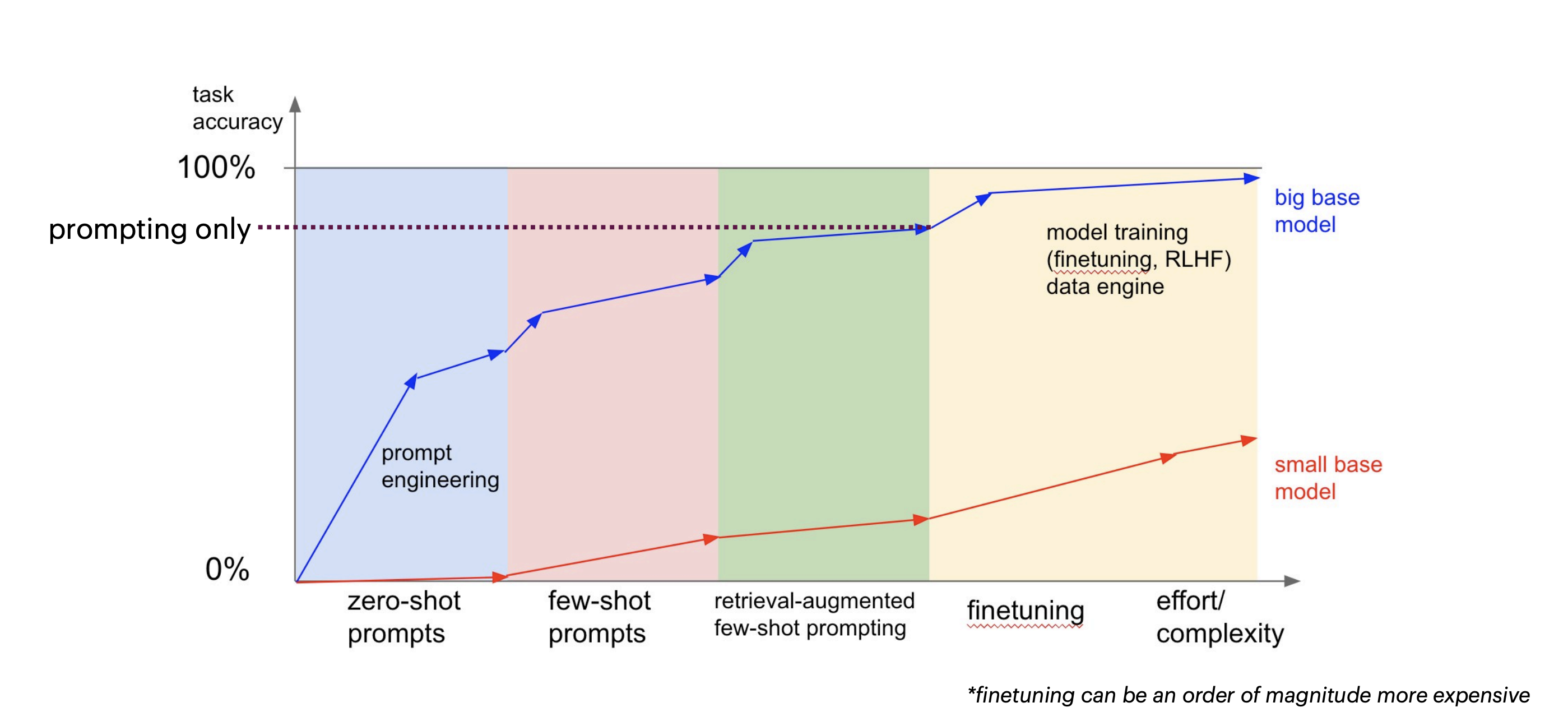 How we can increase the quality of our result through prompting
How we can increase the quality of our result through prompting
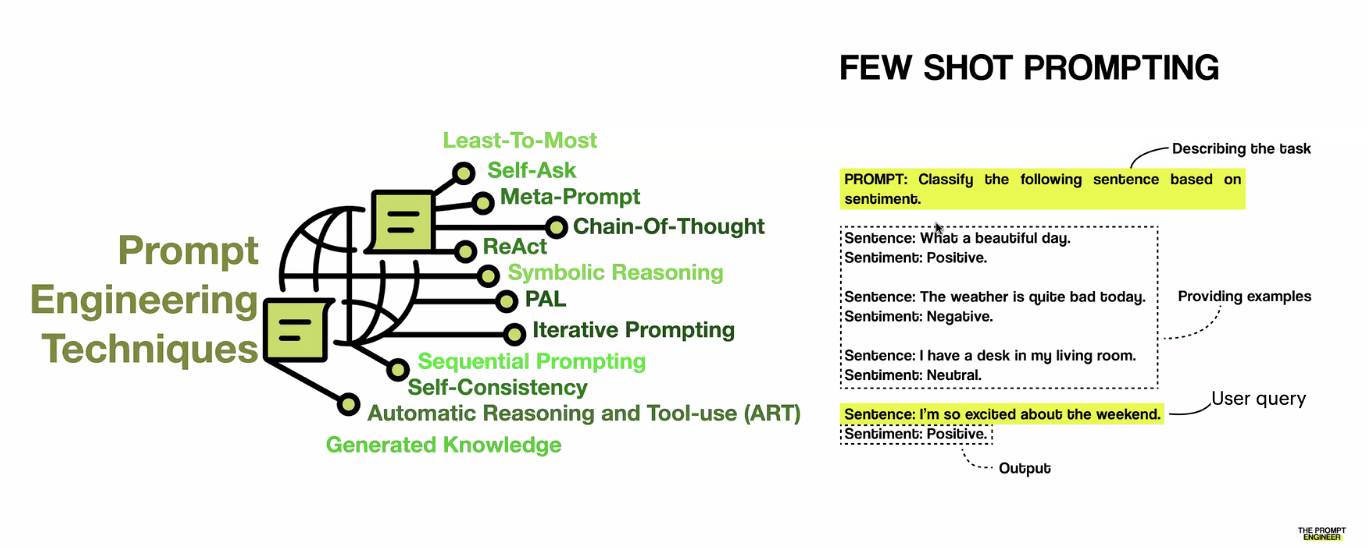
LLM Caching vs Traditional Caching
| Traditional might have: | LLM Serving Systems |
|---|---|
| Separation of compute and storage eg. DRAM and disk | Co-location of compute and state |
| Caching can be useful for any chunk of data - any type of data | Sharing is only useful for prefix - due to autoregressive nature, can only match from beginning of prompt |
| Computation and memory can be predictable | Computation and memory are unknown before execution |
Example Prompt Tree Cache
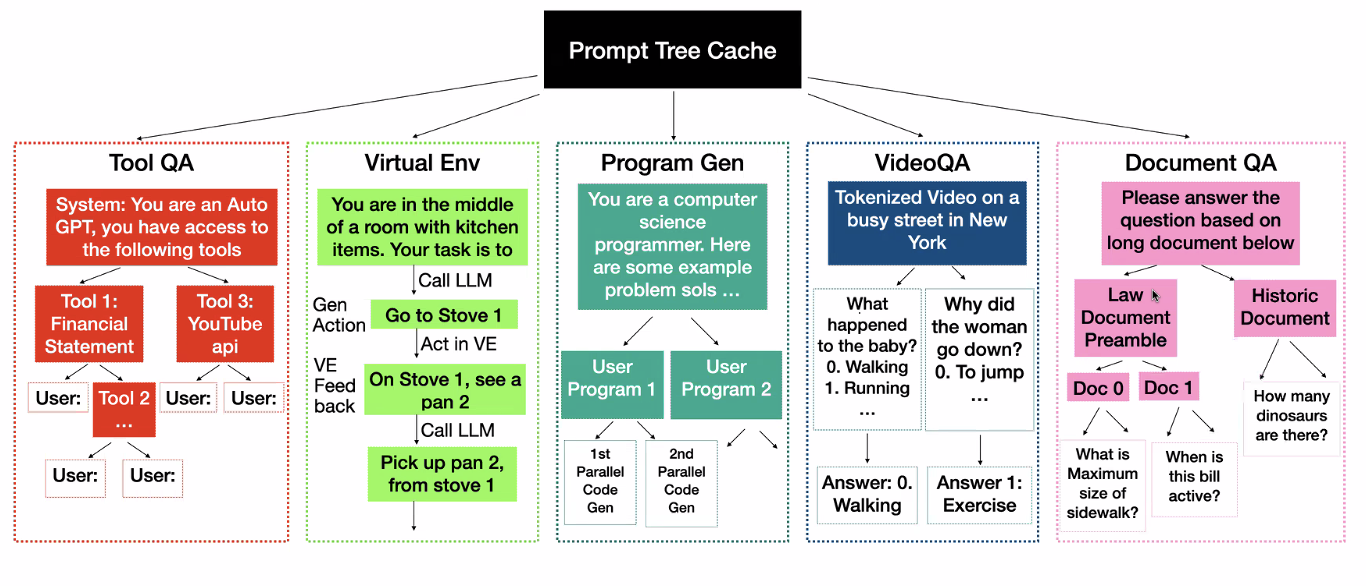
How are real-world prompts like?
High sharing degree

Single GPU example of Prefix Tree
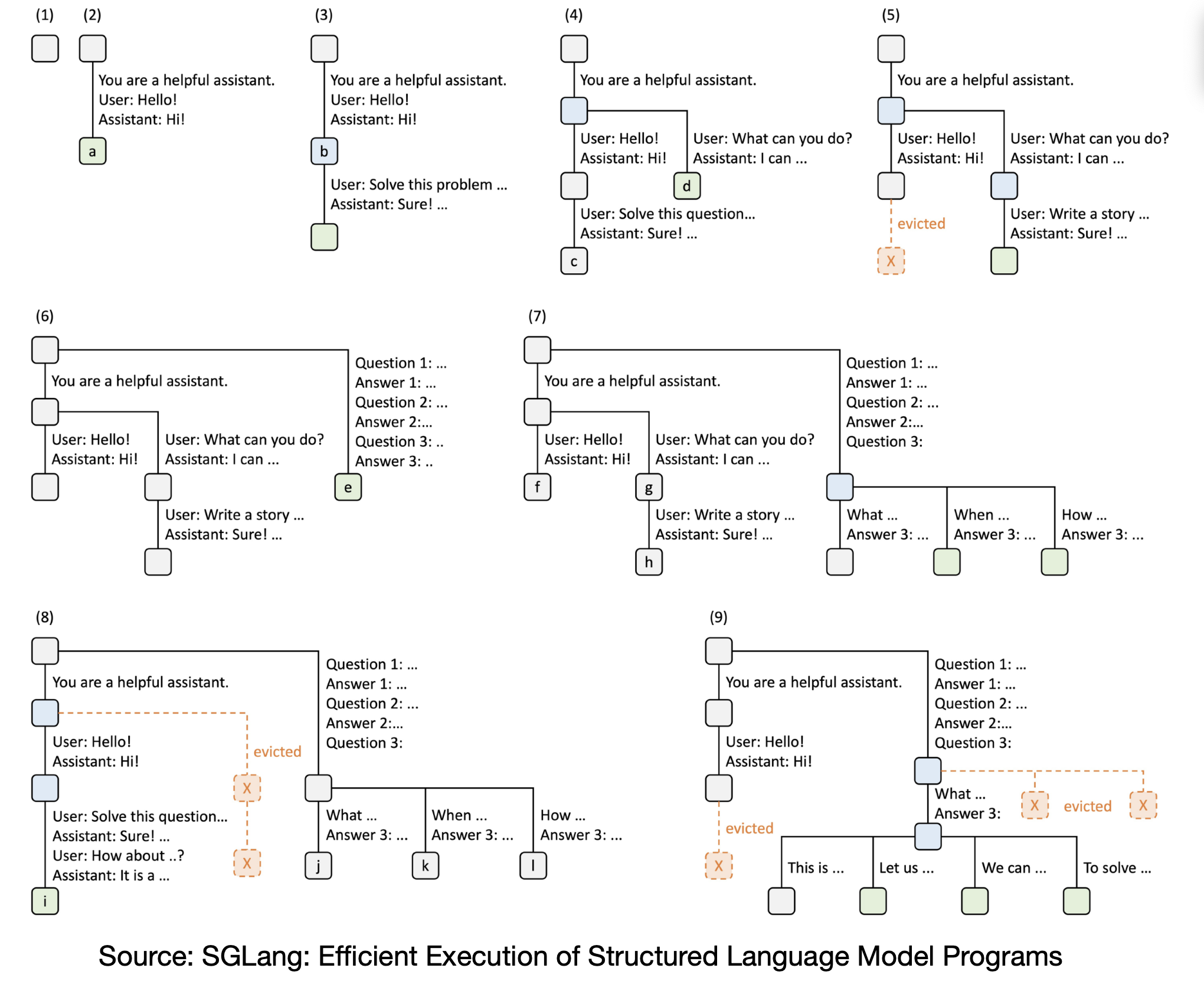
Scheduling comparisons
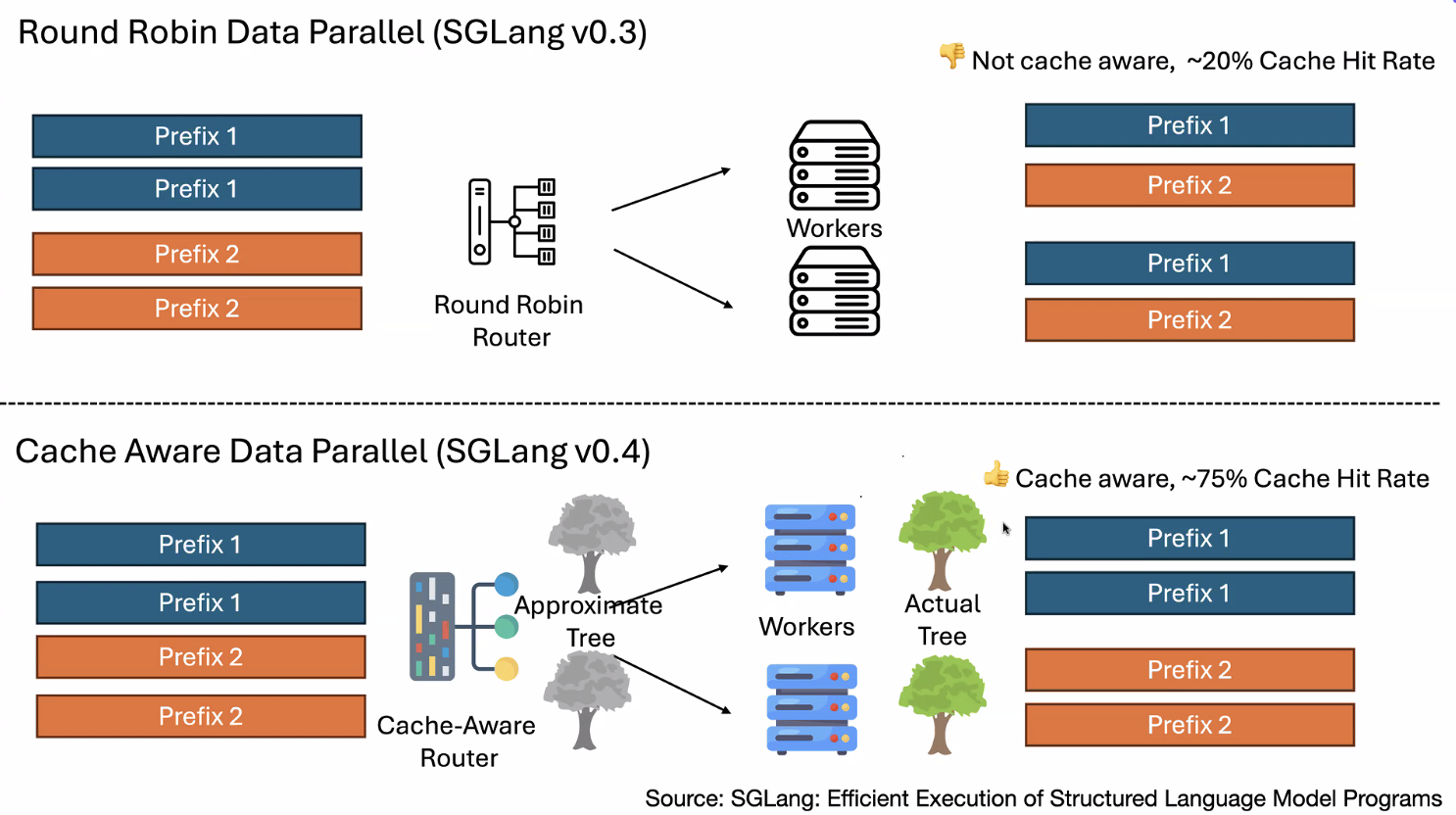
Exploration
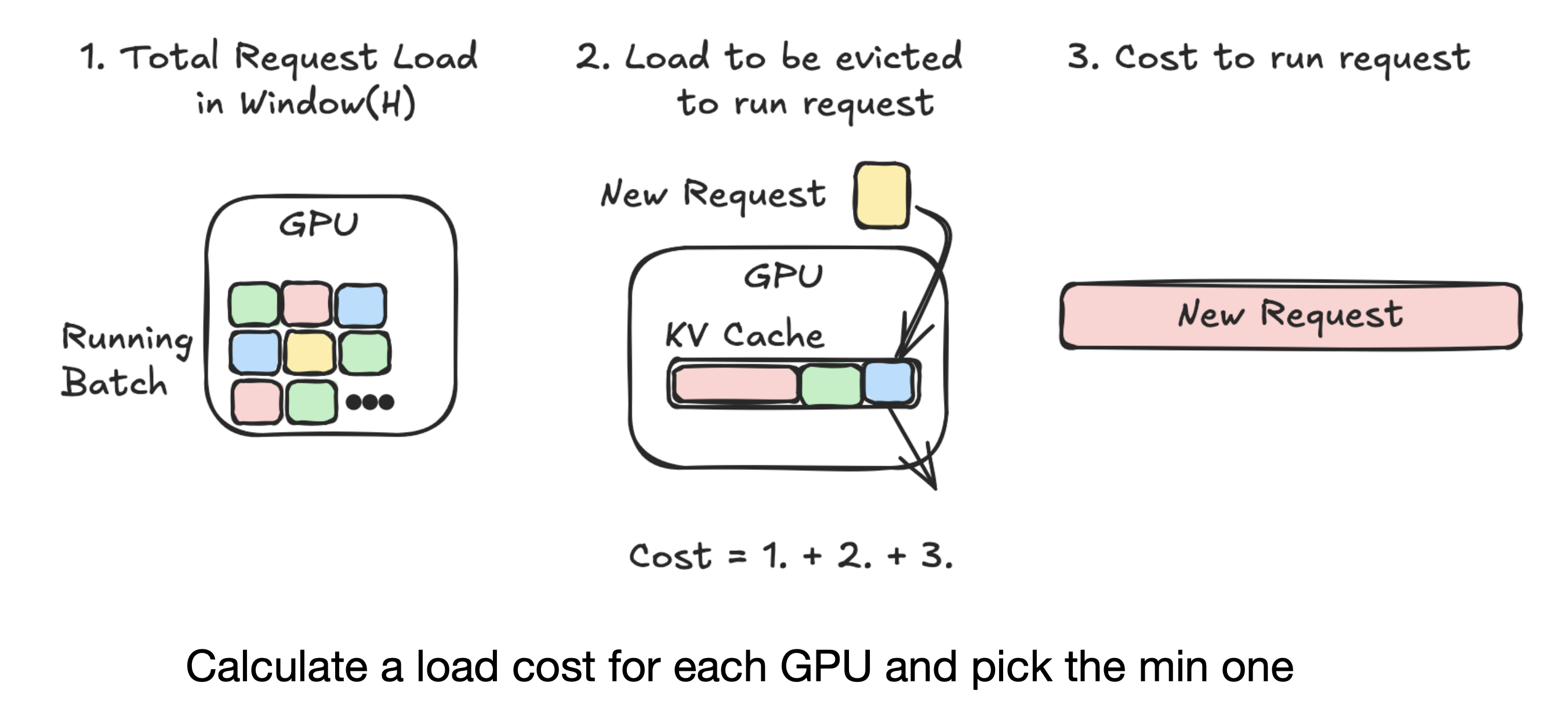
Preble Takeaways
- LLM Serving is getting more expensive using more complex prompting
- Workloads are longer and shared
- Preble(ICLR ’25) enables cache and load to be effectively utilized for performance
- Utilizing E2 scheduler and fair waiting queue