Outline
- GPU Revisited – Why do we need megakernels?
- GPU Programming Model and Execution Model Revisited
- Motivations and Enablers of Megakernel
- How to design mega kernels for modern GPUs?
- Megakernel System Framework
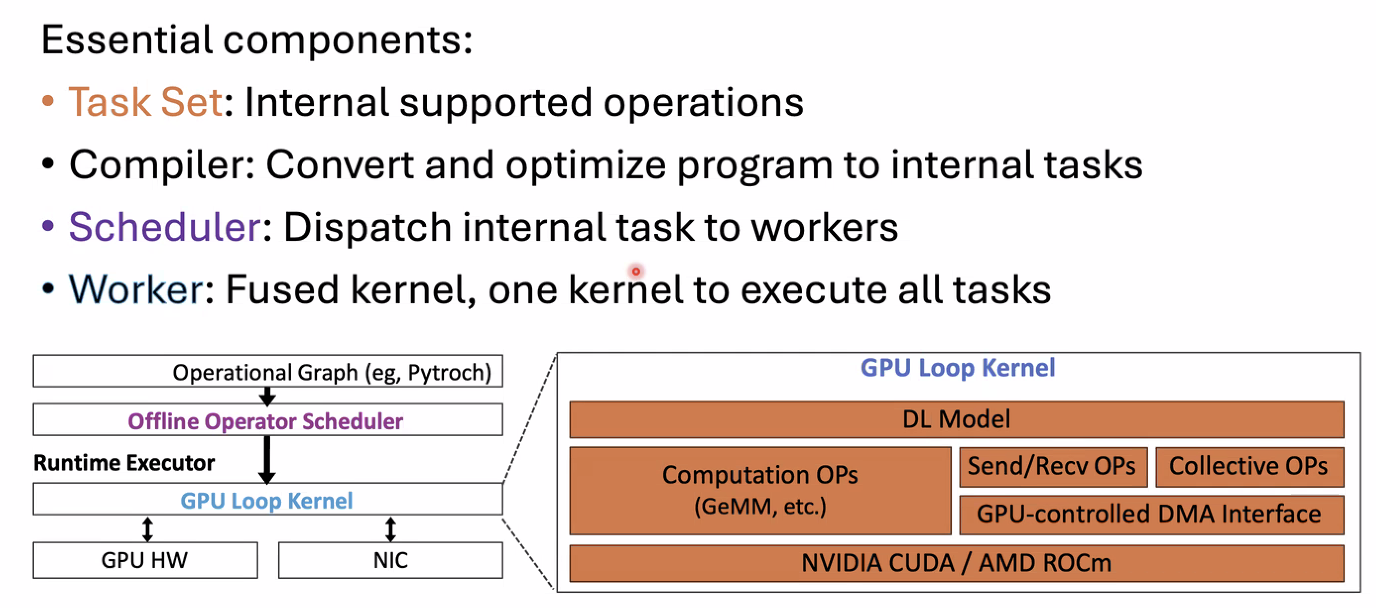
- Megakernel Components
- Understanding the Performance Benefits of Megakernels
GPU Heterogeneous Computing
- Terms:
- Host - The CPU and its memory (host memory)
- Device - The GPU and its memory (device memory)
- GPUs need some special programs to utilize code on the parallel compute of GPU

Simple Processing Flow
- Copy input data from CPU memory to GPU memory
- Load GPU program and execute caching data on chip for performance
- Copy results from GPU memory to CPU memory
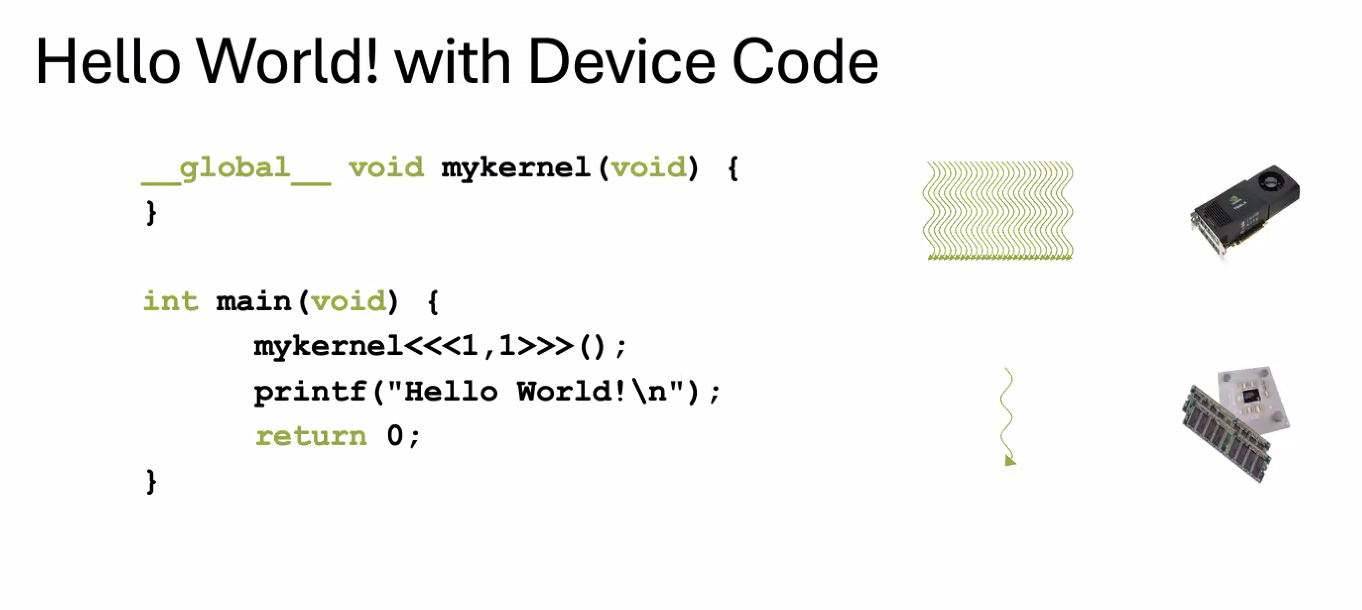 Special code to start the kernel to load code onto GPU
Special code to start the kernel to load code onto GPU
Moving to parallel
GPU computing is about massive parallelism
- so how do we program to make our code run in parallel on the device
- CPU-like code only compute one element at a time
Vector Addition on Device
- With
add()running in parallel we can do vector addition - Terminology: the code of of
add()is executed on massive parallel cores, each core we call it a thread - The programming model is called Single Instruction Multiple Threads (SIMT)
- Each invocation can refer to its block index using
ThreadIdx.x 
- Each invocation can refer to its block index using
- By using
ThreadIdx.xto index into the array, each block handles a different index
Concurrent thread Group (CTA) (todo)
- contains a set of threads that run concurrently
Summary of GPU programming Model
- Programming model
- SIMT - Single Instruction Multiple (Concurrent) Threads
- concurrent - running at the same time, not necessarily parallel
- Single function to instruct
- SIMT - Single Instruction Multiple (Concurrent) Threads
GPU Execution Unit (SM)
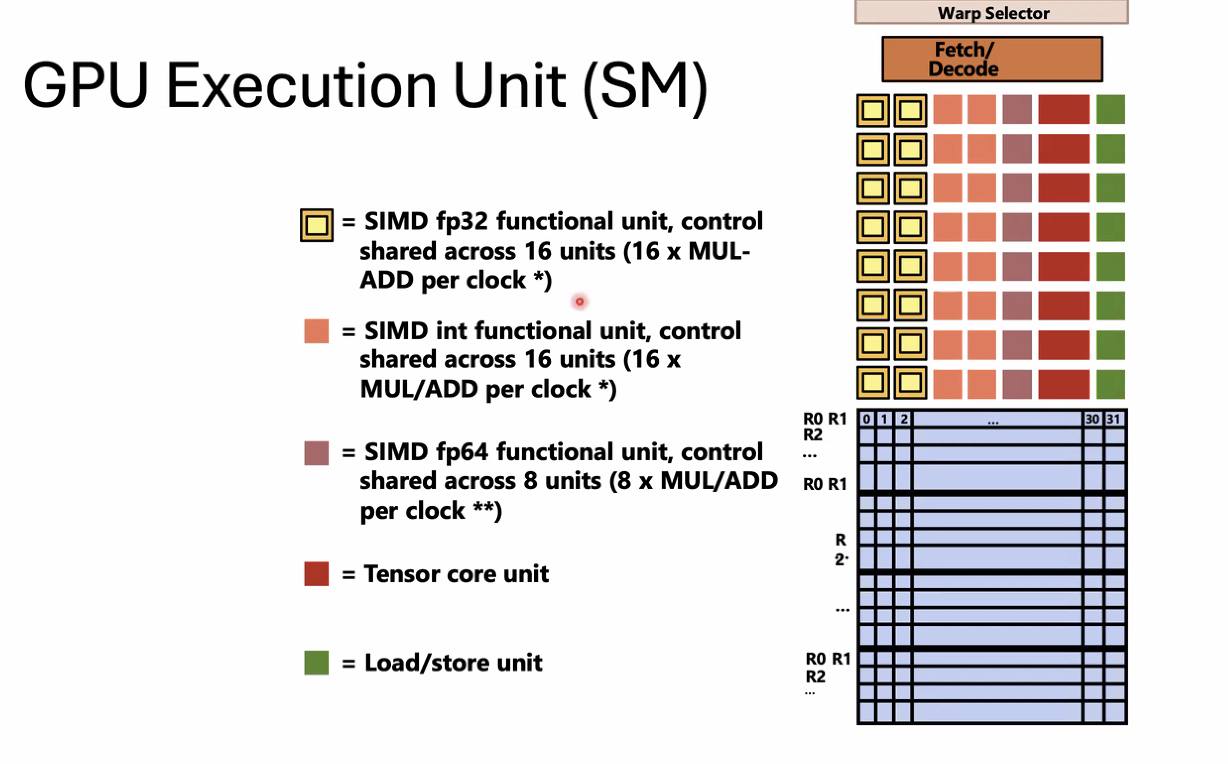
- A group of 32 threads in a thread block is called a warp
- In a CTA, threads 0-31 fall into same warp
- Each sub-core in the V100 is capable of scheduling and interleaving execution of up to 16 warps
- Warp is not part of CUDA programming interface but is an important CUDA implementation detail on modern NVIDIA GPUs
warp as a parallel execution unit
Entire warp of CUDA threads is running this instruction stream
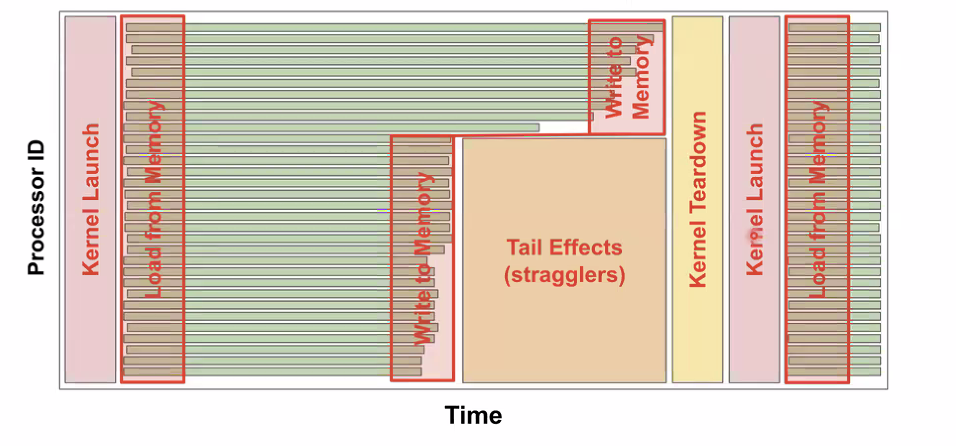
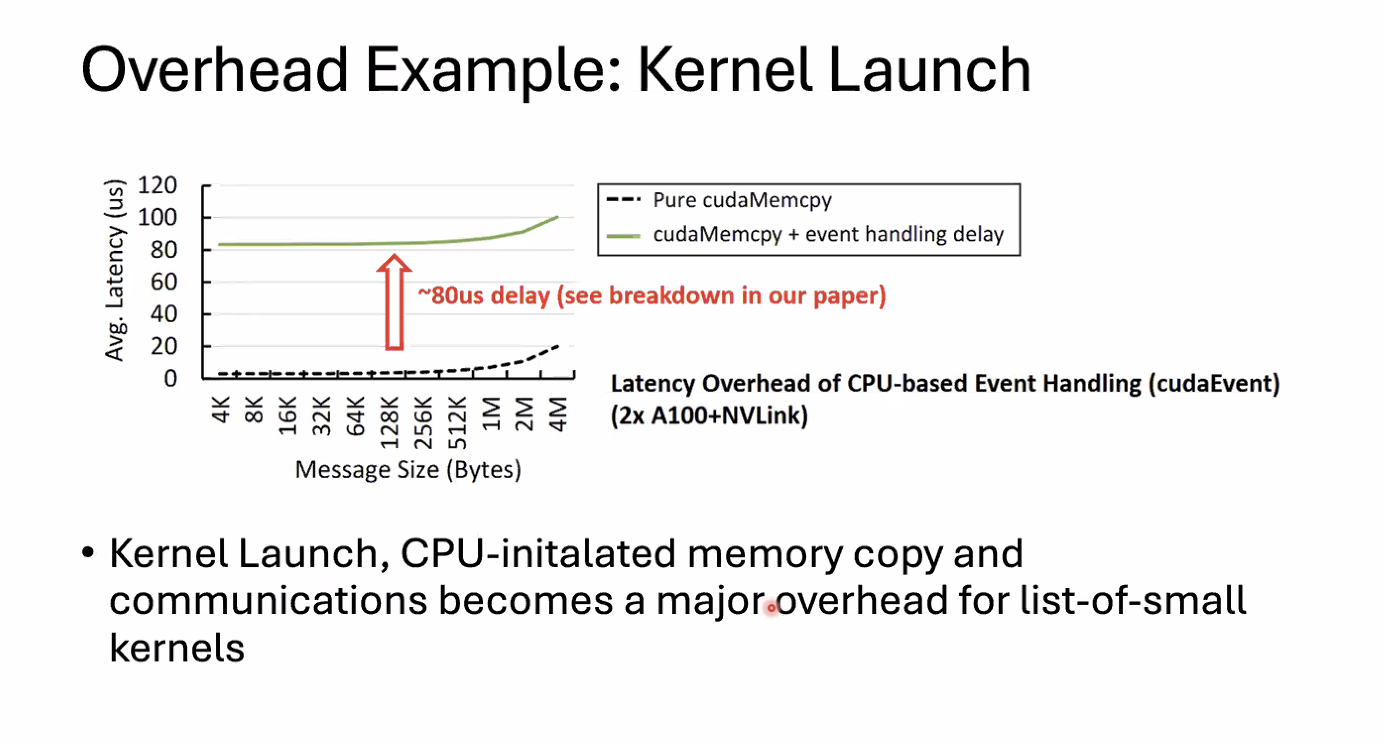
Key Motivation
CPU-based control overhead and opaque hardware scheduling from the kernel overhead.
- CPU will launch kernel and wait for results
- causing GPU idle time
MegaKernels
Combining multiple GPU kernel launches and interkernel communication.
Building a Megakernel system