MIPS R10k
Driving Factors
Avoiding the latency from a cache miss
Challenges
Key Features
- Register renaming
- active and free
What are the structures that allow
- Register renaming?
- In-order commit?
- Correct handling of branch mispredicts/exceptions
IQ Architectures
- many intel processors use an instruction queue
- also MIPS R10k, Alpha 21264+
- Use explicit register renaming
- Registers are not read until instruction issues (begins execution). Register renaming ensure no conflicts (war/waw errors)
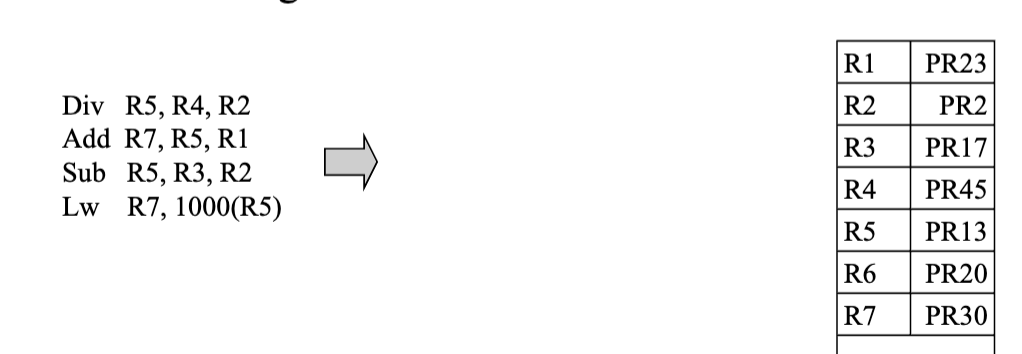
Register renaming
- First Tomasulo example,
- RR due to logical register names to RS entries
- Second Tomasulo example
- RR due to logical register names to ROB entries
- In contrast, R10k type (IQ architectures)
- set of physical registers (larger than logicla register file) and translate all logical register names to physical register names
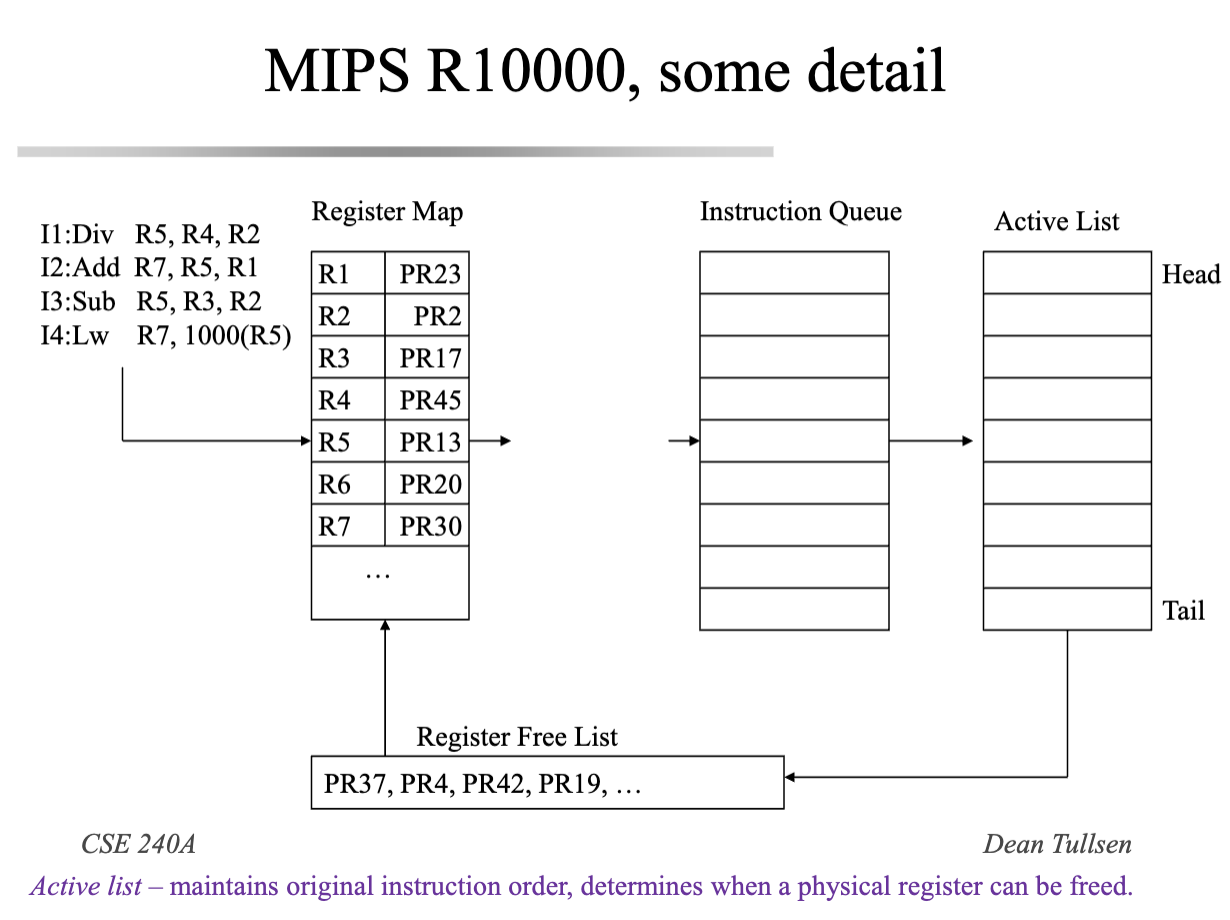
- no need for values in Register map and active list
- somehting with execution order differ from tomosulo
- Active list → ordering, hence similar to tomosulo ROB
- Mispredicts: - 4 bit branch mask to map instr. entries within branch stack,
- flush branch dependent instructions from active list
- restore register from free list (fixed since circular queue)
- MIPS novelty: out of order in commodity processor, tomosulo in specialized machine