Questions
- Q: Compare and contrast protected subsystems in Multics with procedures in Hydra.
- protected subsystems in Multics and procedures in Hydra both utilize a pointer + right bits.
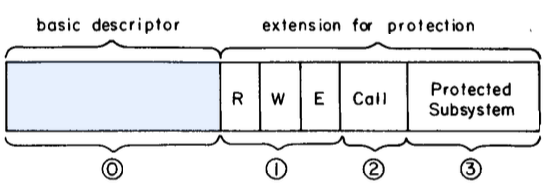
- Control of permission to enter a protected subsystem which has entry points in the segment based on this descriptor.
- Controls on which (hierarchically arranged) protected subsys-
tems may use this descriptor.
- a) the protection domain that they support
- domain per user
- (b) the mechanism for crossing protection domains
- project administrator
- (c) how rights are represented,
- Multics descriptor, has extension bits
- (d) how rights are amplified when crossing domains, and
- permission based, get rights first before crossing so need project administrator
- (e) how the OS determines whether to allow the domain crossing.
Abstract
- Five design principles in Multics design
- Key mechanisms
- Access control lists
- hierarchical control of access specifications
- identification and authentication of users
- primary memory protection
Design Principles
- Five design principles:
- Base the protection mechanisms on permission rather than exclusion
- by default the situation is lack of access and the protection scheme identifies condition under which access is permitted
- Check every access to every object for current authority
- authorization should be stateless. no sessions
- The design is not secret
- mechanisms should not depend on the ignorance of potential attackers
- The principle of least privilege
- every program and every privileged user of the system should operate using the least amount of privilege necessary
- military security rule “need-to-know”
- It is essential that the human interface be designed for naturalness, ease of use, and simplicity, so that users will routinely and automatically apply the protection mechanisms
- Base the protection mechanisms on permission rather than exclusion
- Two functional requirements:
- decentralization of setting of protection specification (not set by a single administrator)
- can’t be a set protection specification like set up HW or by default and static
- assume that some users will require protection schemes not anticipated in the original design
- system should provide a set of primitives for the user, without exercising special privileges, may construct a protection environment which can interpret access requests however he desires
- construct a protected subsystem - collection of programs and data with the property that the data may be access only by programs in the subsystem and the programs may be entered only at designated entry points
- app privacy in mac os
- decentralization of setting of protection specification (not set by a single administrator)
Storage System and Access Control Lists
- Each process has a identifier and the identifier might consist of the personal name of the individual responsible for the action of the process
- this individual is the principle and the identifier principle identifier
- When a process accesses an object in store…
- The principle identifier of the process is compared to the ones in the access control list of the object
- if contains, has access
- else no access
- a principle identifier has multiple components for granting access to groups of users
- The first partition places every individual user of the installation in a separate access control group by himself
- name is personal name
- Second partition is a group called projects
- set of users who cooperate in some activity, such as constructing a compiler
- 1 person can be part of many projects
- third partition, places users in named groups called compartments
- user may operate in any of the named compartments, by designating it at the time of authentication.
- eg. login as admin
- Example:
Jones. Inventory. a- Jones working on a project name “Inventory” designating the personal compartment named “a”
- The first partition places every individual user of the installation in a separate access control group by himself
- Objects with their ACL entry (Ex. Smith.*.* rw ) is comparable to HYDRA capability
- access control indicator = protection bits
Hierarchical Control of Access Specification
- child inherits parent access control list
Authentication of users
Password based
- password not printed on screen :O
- timeout feature If so, the project administrator may indicate that his project will accept login of unauthenticated users.
Primary Memory Protection
- A protected subsystem is a collection of procedures and data bases which are intended to be used only by calls to designated entry points, know in Multics as gates
- you can only enter privileged code through these gates
Multics and HYDRA similarity, memory is reference via pointers + rights bits
Design Comparison
Mechanism vs Policy
- Mechanism - rings and gate segments act as the implementation for protection
- Policy - decided by the system admin for how much protection each ring gets
- eg chmod can changes the policy of the file to read only Saltzer wanted Multics to have mechanisms flexible enough that policies could evolve without rewriting the kernel.
ACLs
- Access control lists were used over capabilities because it contained the full state of who can access a certain object (rights stored with the object).
- With capabilities, the system would have to track the capabilities somehow in relation to an object which is difficult since it’s stored with the user.
Weakness
what might be important? - what did the authors think that was important? - what is different and new from prior work? - do i see these concepts in use today? or why weren’t these ideas adopted? - is there anything generalizable? - ideas that you can apply in a different domain - protection paper example is very generalizable - new abstraction, algorithms, techniques, frameworks? - generalizable typically - identify a new problem space - what is unlikely to be important? - specific example - specific s in evaluation - implementation - proofs - discussion section