HYDRA
Draw parallels to object oriented languages
- we don’t take the HYDRA approach to OS anymore
Design Philosophy
- Rejection of hierarchy - one of the most important in paper
- multiprocessor environment - not as relevant
- separation of policy ← system design principle - important!
- Integration of design & implementation methodology
- social structure of organization resembles OS design
- not as important
- Protection - important!
- Reliability
Goal
Decompose OS into subsystems
protection enforces rules , security = policies
Key Terms
- Protection domains - eg. process vs kernel
- Protected control transfer - eg. syscall
- control transfer = moving between domains
- Rights augmentation - eg. set-user-id in Unix paper
- can increase permissions for object or get higher rights than before
- another ex. password cmd binary
What HYDRA Do
- Abstraction for resources: objects
- object-oriented systems analogy:
- type or class
- well-defined interfaces
- data associated
- pointers to other objects →
- tied closely with capabilities since capabilities is pointer + right bits
- object-oriented systems analogy:
- Abstraction for execution domains: local namespace (LNS)
- what’s instantiated during execution
- object-oriented systems analogy:
- stack frame
- Abstraction for protection: capabilities
- pointer (what object it’s referring to) and rights bits (access control)
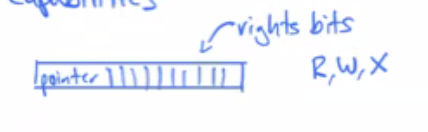
- you can have multiple capabilities to point to a file
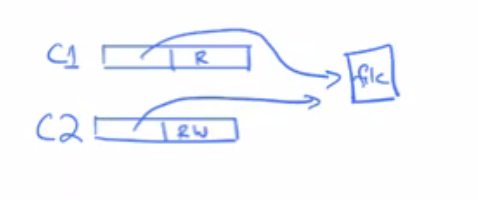
- In hydra there are two different rights:
- Kernel rights
- Auxiliary rights (user defined)
- object-oriented systems analogy:
- private or protected members
Procedures

- Rights checking - procedure checks if capability allows for running the function
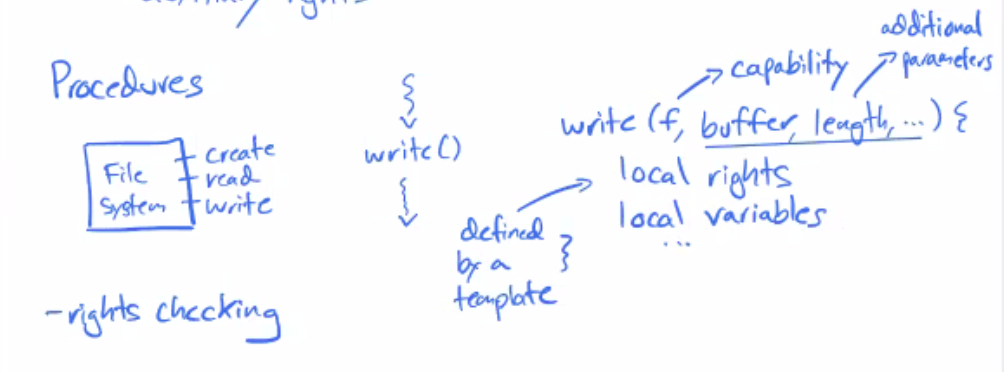
- what are the protection domains in this example?
- One domain is the caller (program that calls)
- One domain is the callee (write function / actual execution)
- what is the protected control transfer?
- calling the function + rights checking
- rights checking makes it protected
- What is the rights augmentation?
- adding additional local rights
Summary
- Capability-based protection mechanism
- Nucleus-like system - primitives mechanisms
Protection
Goals
- abstract model
- unify discussion of protection concepts
Objects - things to protect, resources
- examples:
- process
- files
- domains
- Hydra - objects
Domains -
- static or dynamic domains
- static - Hydra procedure
- dynamic - LNS
- Hydra - LNS, procedure (both have certain rights associated to them)
- Unix - user vs kernel mode, address space, everything accessible by one user
Attributes - protection attributes
- R, W, X
Access Matrix
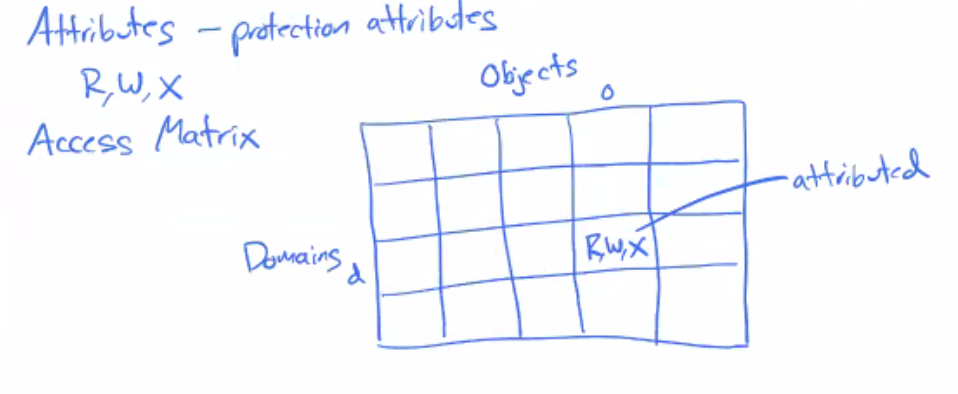
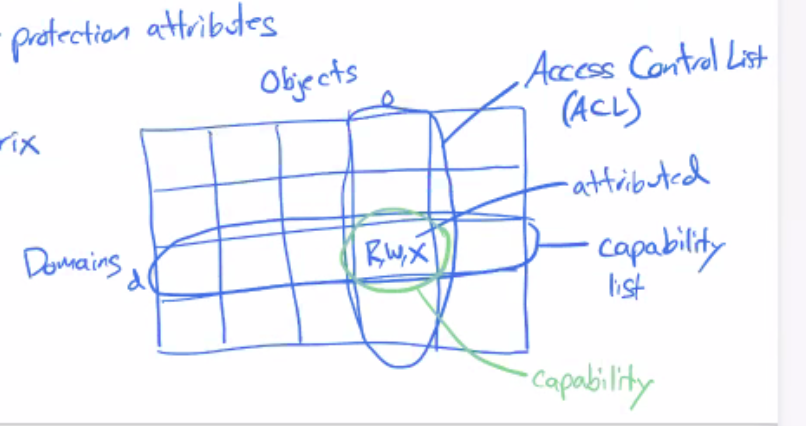
- Access Control List is more obvious - Unix perm bits
Summary
- unified model of protection
- objects, domains, attributes, access matrix
- ACL (columns), capability list (rows)
How to Read Research Papers
- Different high-level strategies
- “How to Read a Paper” S Keshav
- What makes reading paper hard?
- terminology or jargon
- missing context
- going back and forth
- overwhelmed by too many components
- abstract, hard to follow
- identifying cons
- Terminology
- When you get to some term that you don’t understand…
- Highlight it and see if it’s blocking
- is this term blocking my understanding of the paper?
- what do I need to know about this term?
- Getting lost
- highlight it
- look for places where you can hook back onto the paper
- Figuring out what is important
- finish reading → what were the key takeaways?
- what might be important?
- what did the authors think that was important?
- what is different and new from prior work?
- do i see these concepts in use today? or why weren’t these ideas adopted?
- is there anything generalizable?
- ideas that you can apply in a different domain
- protection paper example is very generalizable
- new abstraction, algorithms, techniques, frameworks?
- generalizable typically
- identify a new problem space
- what is unlikely to be important?
- specific example
- specific s in evaluation
- implementation
- proofs
- discussion section