KV Cache
- Memory space to store intermediate vector representations of tokens
- Working set rather than a “cache”
- The size of KV Cache dynamically grows and shrinks
- A new token is appended in each step
- Tokens are deleted once the sequence finishes
- Additional info: https://medium.com/@joaolages/kv-caching-explained-276520203249
Key Insight
Efficient management of KV cache is crucial for high-throughput LLM serving
- The size of KV Cache dynamically grows and shrinks
- A new token is appended in each step
- Tokens are deleted once the sequence finishes
Memory Waste
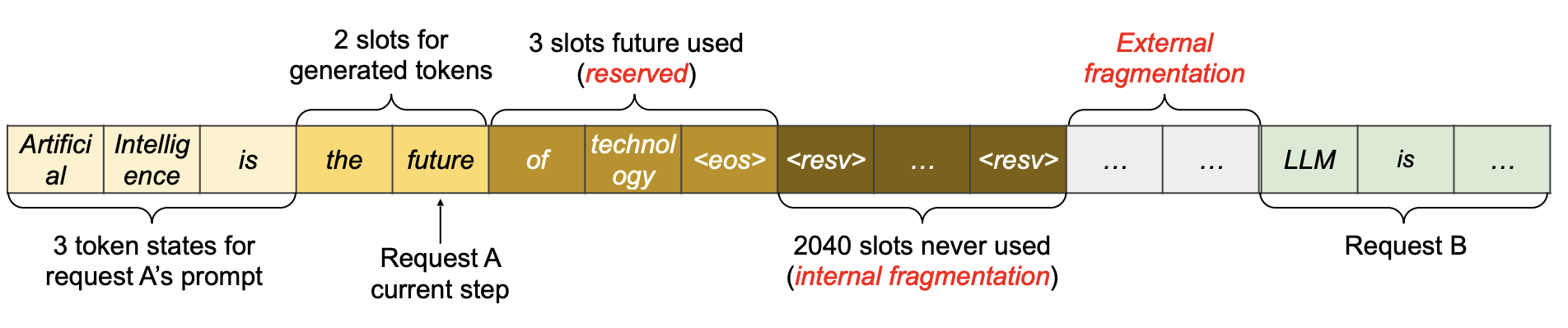
- Reservation: not used at the current step, but used in the future
- Internal fragmentation: over-allocated due to the unknown output length.
- External fragmentation: due to different sequence lengths.
KV vs Classical Page table
- Classical Page table multiple levels, block table is one level
- For GPU KV cache, request batches are contagious. Tokens only grows one way in memory so we can have a flat entry. You never free memory In contrast to classical page tables, KV Cache can have a flat lookup table because entries only grow
What We Have Learned about LLM Scheduling It is a tradeoffs
- Scheduling overhead can be significant and dominate e2e performance
- Absolute scheduling overhead grow with both input size and task complexity
- Input: vLLM scheduling grows with token and request counts (hint: implement in native language)
- Complexity: SGLang overhead with prefix cache (esp. with big prefix tree)
- Relative scheduling overhead is higher when other parts in e2e is faster
- Faster model forwarding, less frontend processing, etc.
- Chunked prefill makes scheduling overhead higher (both absolute and relative)
- Multi-step scheduling lowers overall scheduling overhead but has its tradeoffs
- Faster CPU and slower GPU reduce scheduling overhead (cmp. results on our servers with A6000 GPUs)
Ideas with no tradeoffs to system
- Rewrite to faster lang
- not if you don’t consider engineer ramp up and complexity
- Async scheduling