Definiton
Data is organized into tables.
SQL is used to query from relational databases
Design notes
- Good for transaction, intricate queries and ensuring data integrity
- Follows ACID properties
- Scaling up techniques
- Master-Slave replication
- allows data to be replicated from one DB(master) to other DB(slave)
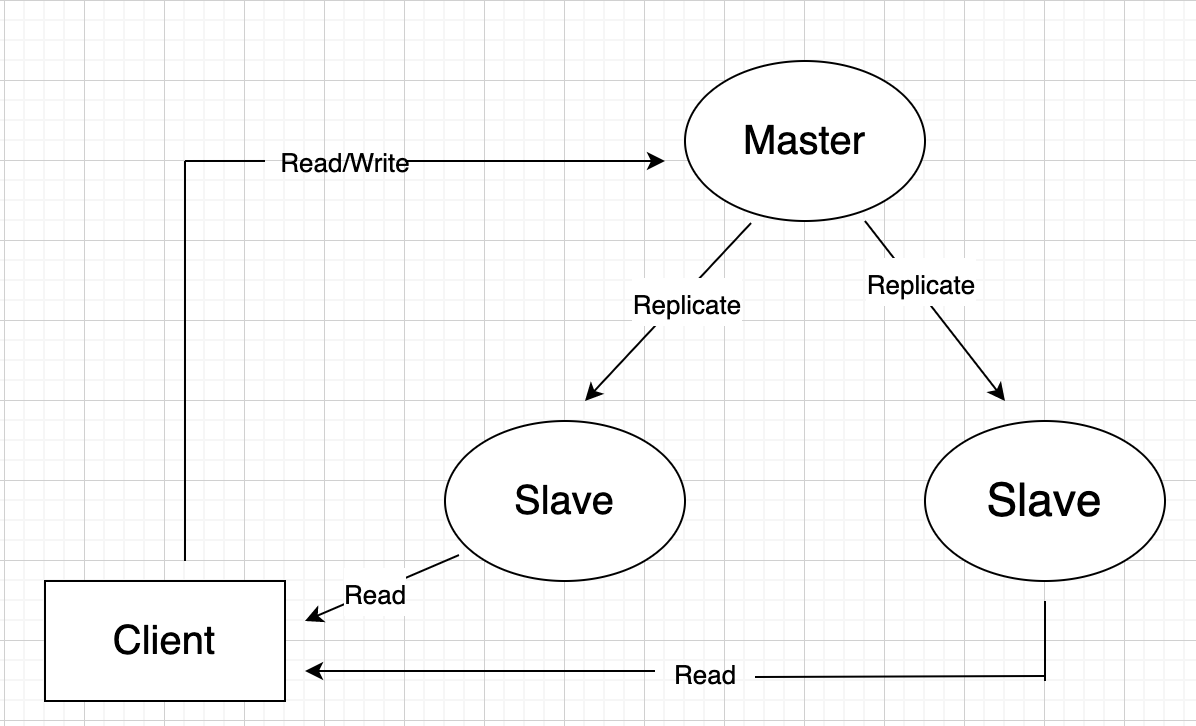
- Advantages:
- read load spread among slaves
- analytic applications can read from slave without affecting master
- backup of the database is available readily without affecting the performance of the master
- Disadvantages:
- all writes are made by master, performance issues
- additional logic for promotion
- load is top heavy
- potential loss of data if master fails
- Master-Master
- Both masters perform read and write operations, but need to coordinate on the write operations
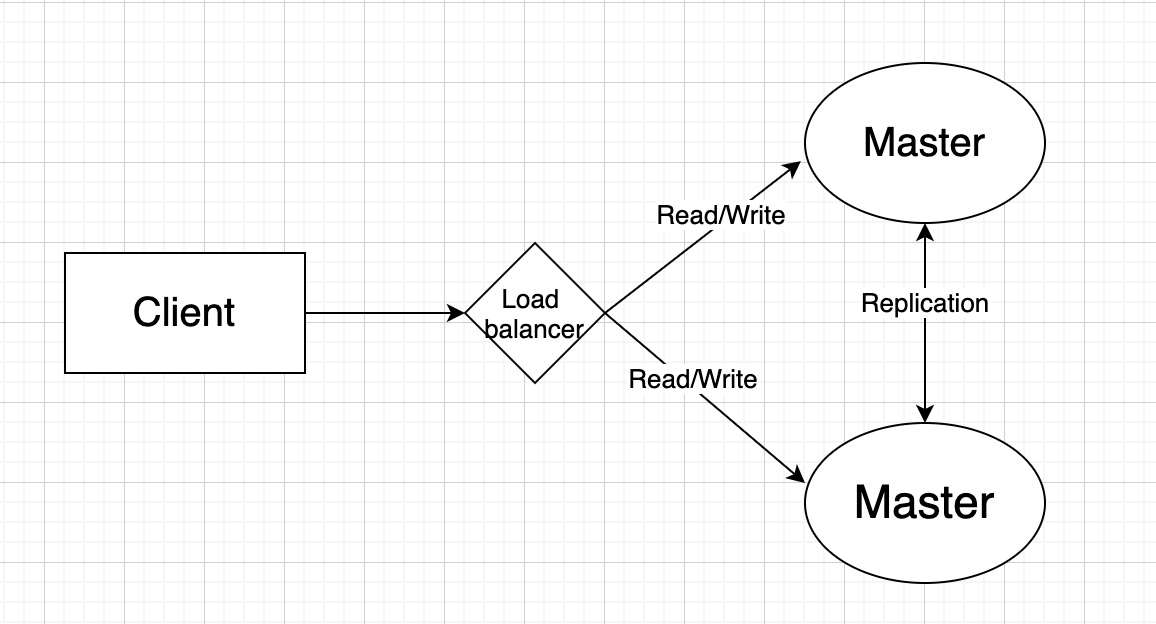
- Advantages:
- Write load is shared
- Application and read from both masters
- Handles simple fault handling by switching to other available master
- Disadvantages:
- need to maintain consistency
- need a load balancer to distribute writes or application logic
- loosely consistent, violating ACID or increase latency due to synchronization
- potential loss of data
- Federation
- Federation or functional partitioning splits up the database based on functionality and combines it in a layer above

- Advantages:
- Faster read-write
- Decreased latency
- Disadvantages:
- Not effective if schema has huge number of functions (or tables)
- Join operations from two DB is complex and expensive
- Increase in complexity
- Meed to update application logic on migration
- Sharding
- Horizontal partitioning of data by subset of data
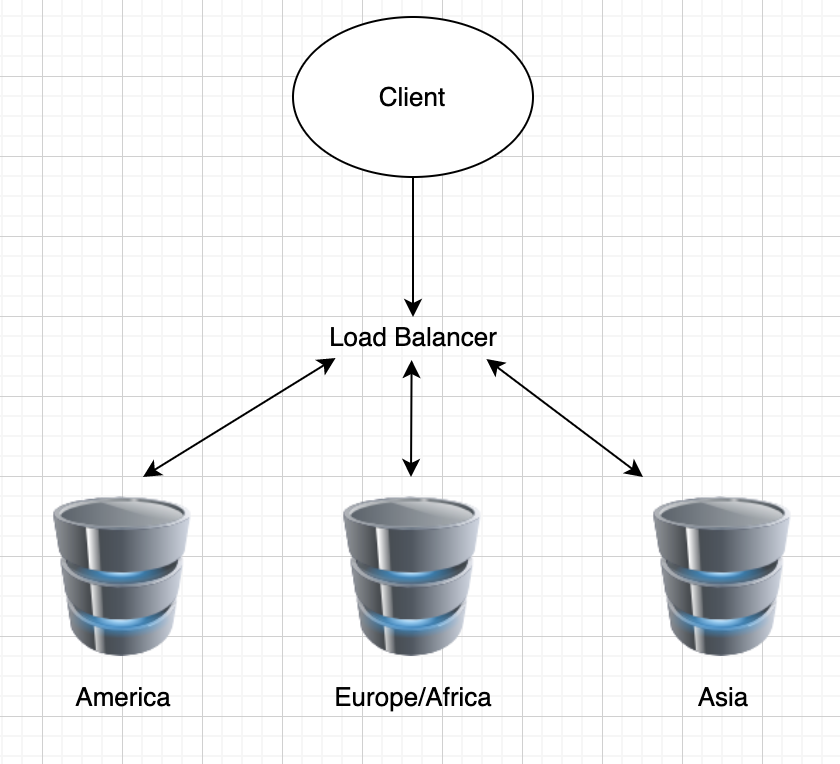
- Advantages:
- High availability (replication)
- Faster querying (less traffic per DB)
- Increasing write throughput (parallel writes)
- Disadvantages:
- Uneven load (bias on DB)
- increased complexity
- less support
- Master-Slave replication
Sources: